Operating Costs Calculation: Unlocking Financial Health and Sustainability
7 Reading minutes
Understanding operating costs calculation is crucial for any business, as it provides a clear picture of the financial health and sustainability of a project.
In this article, we’ll delve into the key aspects of operating costs, exploring their types and offering a step-by-step guide on how to calculate them accurately.
What are the Operating Costs?
The operating costs refer to the total expenditures incurred during the regular operation and maintenance of a project or business.
These costs encompass a wide range of financial outlays necessary for day-to-day functioning and include both direct and indirect expenses.
Direct operating costs calculation typically involve the production or service delivery process, while indirect costs cover the general overhead essential for overall business operations.
In essence, the project’s operating costs include various elements such as raw materials, labor, utilities, rent, salaries, insurance, and other expenses essential to sustaining regular business activities.
Calculating and understanding these costs is pivotal for effective financial management, aiding businesses in making informed decisions, budgeting, and ensuring the overall economic viability and success of the project.
Types of Operational Costs
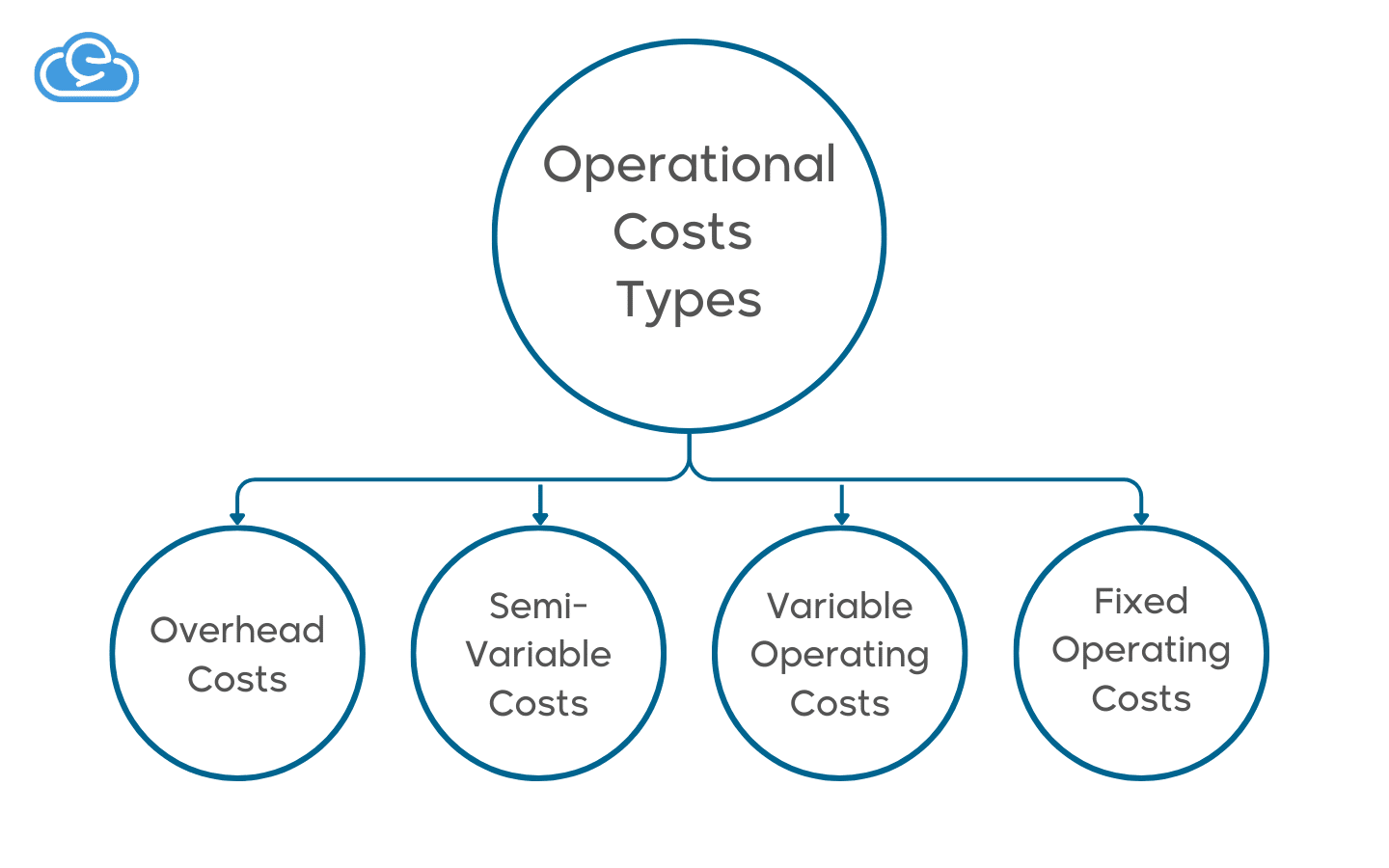
Operational costs include a wide range of expenses covering various aspects of project operations. It can be classified into:
Fixed Operating Costs
Fixed operating costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production or business activity. These costs do not fluctuate with changes in output or sales volume, making them stable and predictable.
Common examples of fixed operating costs include rent or lease payments, insurance premiums, salaries of permanent staff, property taxes, and equipment depreciation.
Despite variations in production or sales, fixed operating costs remain consistent, providing a baseline that businesses must cover to sustain operations.
Variable Operating Costs
Variable operating costs play a pivotal role in project economics, directly influenced by production dynamics and market shifts.
These costs, such as packaging materials, direct labor, utilities, shipping, and raw materials, fluctuate in sync with changes in production volume and sales.
The adaptability of variable costs to project needs and market demands provides businesses with flexibility.
Managing these dynamic expenses is essential for optimizing project economics, ensuring adaptability, and fostering financial resilience in a changing business landscape.
Semi-Variable Costs
Semi-variable costs, also known as mixed costs, exhibit characteristics of both fixed and variable costs.
These expenses consist of a fixed component that remains constant within a certain range of activity but may change when production levels or business operations surpass a specific threshold.
For example, utility bills often have a fixed basic charge along with a variable component based on usage. Semi-variable costs present a challenge for businesses as they require careful analysis to understand and manage effectively.
Overhead Costs
Overhead costs, also referred to as indirect costs, encompass all the expenses associated with running a business that are not directly tied to the production of goods or services.
These costs are essential for day-to-day operations and support the overall functioning of the business. Overhead costs include items such as rent for facilities, utilities, administrative salaries, office supplies, maintenance, and other general operating expenses.
Unlike direct costs, which are specifically attributable to production, overhead costs are incurred regardless of the level of output and are distributed across various business activities. Efficient management of overhead costs is crucial for maintaining financial stability and optimizing overall business performance.
How to Calculate Operating Costs?
Operating costs are calculated using the following equation:
Total Operating Costs = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) + Operating Expenses (OPEX)
It is important to follow a systematic approach to be able to accurately determine operational costs. Below are some of the main steps followed in calculating operational costs:
Calculating the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
To determine the COGS, identify the direct costs involved in production. For instance, if you own a bakery, consider raw material costs, packaging, and other direct expenses. Assuming these amount to $10,000 per month, this figure becomes a crucial component in your operating costs calculation.
Operating Expenses Account (OPEX)
Calculate indirect costs associated with day-to-day operations, such as rent, utilities, and salaries of non-production employees. Let’s assume your monthly operating expenses are $5,000.
Add Operating Expenses to COGS
Combine the calculated COGS of $10,000 with operating expenses of $5,000 to determine your final operating costs calculation.
Example of Calculating Operational Costs
Let’s break down the process of operating costs calculation using a hypothetical scenario where you own a bakery.
1. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
In this step, you determine the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) by accounting for the direct costs associated with producing baked goods.
This includes expenses for raw materials, packaging, and other directly attributable costs. For instance, let’s assume your bakery’s raw material costs, packaging, and related direct expenses amount to $10,000 per month.
2. Calculate Operating Expense Calculation (OPEX)
Next, you calculate the Operating Expenses (OPEX), which includes indirect costs associated with running the bakery but not directly tied to production.
Examples of operating expenses are rent, utilities, salaries of employees not directly involved in production, and other miscellaneous costs. Suppose your monthly operating expenses, including rent, utilities, and non-production salaries, sum up to $5,000.
3. Sum Up Total Operating Costs
To obtain the total operating costs, you simply add the calculated COGS to the OPEX. Using our example figures:
COGS: $10,000
OPEX: $5,000
Total Operating Costs = COGS + OPEX
Total Operating Costs = $10,000 + $5,000 = $15,000
So, in this scenario, the total operational costs for your bakery would be $15,000 per month. This comprehensive approach to operating costs calculation ensures that both direct and indirect expenses are considered, providing a clear and accurate representation of the financial requirements for sustaining your bakery’s day-to-day operations.
Tips for Accurately Calculating Operating Costs
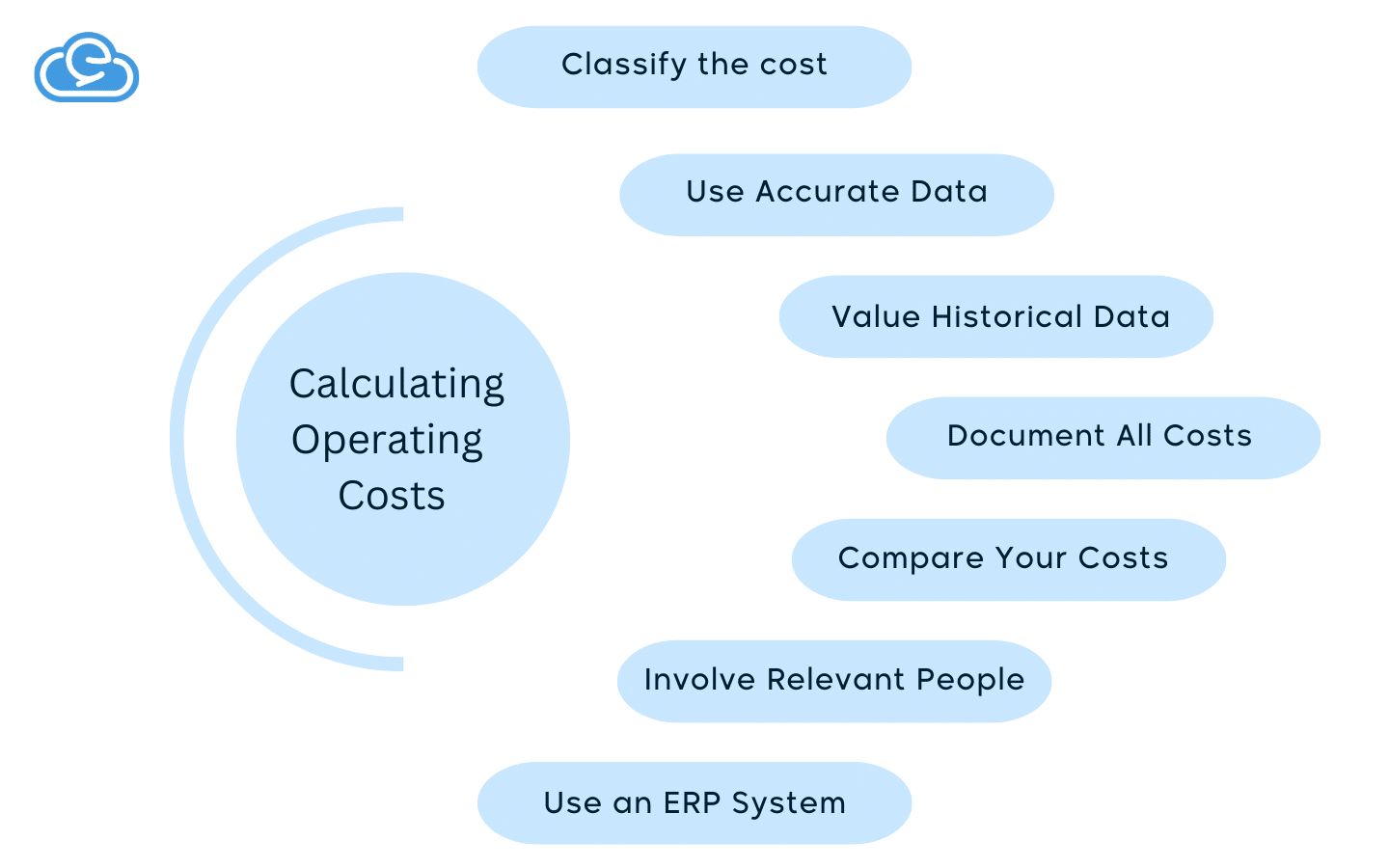
Determining your organization’s operational costs is a matter that entails many decisions, so it is necessary to be precise when calculating these costs. Below are some tips that will help you with that.
1- Classify the Costs
In this step, it’s crucial to systematically categorize your expenses into different types: fixed, semi-variable, and overhead.
Fixed costs remain constant, semi-variable costs vary within a certain range, and overhead costs support general operations. This classification helps create a nuanced view of your financial landscape, enabling better control and strategic decision-making.
2- Use Accurate Data
Accuracy is paramount when dealing with financial data. Ensure that the information you use for calculations is current and precise.
Outdated or inaccurate data can lead to flawed analyses and decision-making, potentially impacting the overall financial health of your project or business.
3- Value Historical Data
Historical data serves as a valuable guide for predicting trends and understanding patterns in your expenses.
Analyzing historical operating costs calculation provides insights into seasonality, cyclical patterns, and potential cost fluctuations. Ignoring historical data could mean missing out on valuable context that aids in making informed financial decisions.
4- Document All Costs
Maintain a meticulous record of all expenses, regardless of their size. Every cost, whether fixed, variable, or overhead, contributes to the overall financial landscape.
Documentation not only ensures transparency but also facilitates a comprehensive analysis of where your resources are allocated, aiding in identifying potential areas for cost optimization.
5- Compare Your Costs
Benchmarking your costs against similar businesses or industry standards is a strategic approach. This comparison helps you understand how your expenses align with market norms, revealing potential areas for improvement or areas where your business excels.
It provides a broader context for evaluating the efficiency and competitiveness of your cost structure.
6- Involve Relevant People
Collaboration is key. Involve relevant stakeholders, department heads, or individuals responsible for different aspects of the business in the cost analysis process and operating costs calculation.
Their insights and knowledge can provide a more holistic understanding of costs and potentially uncover areas for improvement or efficiency gains.
7- Use an ERP System
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system like “Edara” streamlines the process of managing and analyzing operating costs calculation.
ERP systems integrate various business functions, providing a centralized platform for real-time data access.
“Edara” specifically can enhance accuracy, efficiency, and overall effectiveness in handling financial information, contributing to more informed decision-making and streamlined operations.
Simplify Accurate Cost Calculation with “Edara”
“Edara,” your comprehensive business solution, seamlessly integrates your organization’s various departments into a centralized system designed for accurate operation cost calculation.
Here’s how “Edara” ensures precision in defining cost categories and provides valuable insights into your business’s financial aspects:
Centralized Connectivity
“Edara” connects your organization’s departments, ensuring a unified approach to cost management. By centralizing data, it eliminates silos and fosters collaboration, allowing for a more accurate and operating costs calculation.
Detailed Financial Reports
“Edara” empowers you with detailed reports that break down the intricacies of your business’s financial landscape. From fixed costs to overheads, these reports provide a comprehensive understanding of your expenditure, facilitating informed decision-making.
Anywhere, Anytime Accessibility
Edara’s cloud-based infrastructure ensures that your financial data is easily accessible from anywhere, at any time. Whether you’re in the office, on the go, or working remotely, you can effortlessly access the information you need for precise cost analysis.
Data Accuracy Assurance
“Edara” is designed to provide accurate data about your organization’s costs. Through robust data management and validation processes, it minimizes the risk of errors, ensuring that the financial insights you gain are reliable and trustworthy.
Incorporating Edara into your business operations not only simplifies the process of operating costs calculation but also enhances accuracy, accessibility, and overall financial transparency.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve unraveled the complexities of operating costs, offering insights into types, calculation methods, and crucial tips. From understanding project costs to dissecting fixed, semi-variable, and overhead expenses, we’ve provided a roadmap for financial health.
The step-by-step calculation process and practical tips underscored the importance of accuracy. The integration of “Edara” emerged as a solution, streamlining operations with its connectivity, detailed reports, anytime accessibility, and data accuracy.
In essence, by embracing tools like “Edara,” businesses can simplify operating costs calculation, ensuring accuracy and transparency. This mastery of financial precision positions organizations for informed decision-making and sustained success.
Request a demo to learn more about “Edara”.
Related articles
Calculating the Cost of Goods Sold for Efficient Financial Management
In the intricate world of business finance, calculating the cost of goods sold (COGS) is a crucial aspect that provides insight into the direct expenses associated with the production of…
