Navigating KSA E-invoicing Phase 2: Key Highlights and FAQs Unveiled
8 Reading minutes
In a significant leap toward digital transformation, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has ushered in the second phase of its electronic invoicing system, aptly named “the integration phase.”
KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 mandates taxpayers to seamlessly connect their electronic invoicing systems with the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority platform, known as the “Fatoora Platform.”
In this article, we learn in detail about this stage and present the most frequently asked questions about it.
What is “KSA E-invoicing Phase 2”?
The second phase of electronic invoicing in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia marks a pivotal stage in the nation’s digital transformation journey.
Termed “the integration phase,” this stage mandates a crucial connection between taxpayers’ electronic invoicing systems and the authoritative Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority platform, commonly referred to as the “Fatoora Platform.”
Taxpayers are tasked with applying these procedures to guarantee the seamless and effective integration of their systems with the overarching invoice platform.
As Saudi Arabia paves the way for a more technologically advanced financial landscape, this phase stands as a crucial bridge between traditional practices and the streamlined efficiency offered by electronic invoicing.
Target Segment for the Second Phase Application
The KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 encompasses all taxpayers from the first phase, introducing a systematic transition based on groups identified by the Authority.
Taxpayers receive notifications at least six months before the specified implementation date.
The Second Phase of the KSA E-invoicing Waves
The Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority announced the waves included in the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2, which are as follows:
Integration Wave 1
Taxpayers with annual revenues subject to value-added tax exceeding 3 billion Saudi riyals in 2021. Implementation began on January 1, 2023, and continued until June 2023.
Integration Wave 2
Taxpayers with annual revenues exceeding half a billion Saudi riyals in 2021. The system was applied from July 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023.
Integration Wave 3
Taxpayers with annual revenues over 250 million Saudi riyals in 2021 or 2022. The application period commenced on October 1, 2023, and will conclude on January 31, 2024.
Integration Wave 4
Taxpayers with annual revenues exceeding 150 million Saudi riyals in 2021 or 2022. Electronic invoicing implementation started in February 2023 and will continue until February 29, 2024.
Integration Wave 5
The fifth wave in KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 comprises taxpayers whose annual revenues subject to value-added tax surpass 100 million Saudi riyals in either 2021 or 2022.
The implementation period for this wave commenced on December 1, 2023, and is set to conclude on March 31, 2024.
Integration Wave 6
This wave encapsulates taxpayers with annual revenues subject to a value-added tax exceeding 70 million Saudi riyals in 2021 or 2022.
This wave enters the electronic invoicing phase on January 1, 2024, embarking on a journey that spans until April 30, 2024.
Integration Wave 7
The seventh wave encompasses individuals and entities with annual revenues subject to VAT surpassing 50 million Saudi riyals in either 2021 or 2022.
Commencing on February 1, 2024, the process for this wave unfolds, with the application period drawing to a close on May 31, 2024.
Integration Wave 8
In the eighth wave, taxpayers with annual revenues subject to value-added tax exceeding 40 million Saudi riyals in 2021 or 2022 navigate the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2.
Their journey begins on March 1, 2024, and concludes on June 30, 2024.
Integration Wave 9
The ninth wave brings together entities and individuals whose annual revenues subject to VAT exceed 30 million Saudi riyals in 2021 or 2022.
Their application period spans from June 1, 2024, to September 30, 2024, signifying the concluding phase of the electronic invoicing rollout.
KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 Requirements
The successful implementation of the second phase of electronic invoicing in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia necessitates meticulous compliance with specific requirements set forth by the Zakat, Income, and Customs Authority.
These requirements are encapsulated in some fundamental points:
1. Providing an E-Invoice Solution Capable of Connecting to the Internet
To align with the digital framework, taxpayers are required to employ an accounting program that demonstrates seamless connectivity to the Internet.
This ensures the efficient flow of data between their internal systems and the broader electronic invoicing ecosystem.
Read: Top 5 Prominent ZATCA-Approved Accounting Software Solutions
2. Establishing API Integration for E-Invoice Solutions with Authority’s Publication
The integration between the chosen accounting program and the “Fatoora” platform is paramount in KSA E-invoicing Phase 2.
Taxpayers must ensure the successful establishment of this integration to enable real-time data exchange and secure integration with the central electronic invoicing platform.
3. Including All Additional Fields in the Electronic Invoice for the Second Stage
To enhance data accuracy and completeness, electronic invoices in the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 must incorporate all additional fields specified by the Zakat, Income, and Customs Authority.
This inclusivity ensures that the electronic invoices generated are in full compliance with regulatory standards.
4. Issuing and Saving Invoices in XML or PDF/3A Format, Including XML Format
The prescribed format for issuing and saving invoices during the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 includes the XML format or PDF/3A format, with a specific emphasis on XML.
Taxpayers are mandated to adhere to this format requirement to facilitate standardized data exchange and enable seamless interoperability within the electronic invoicing ecosystem.
By adhering to these four crucial requirements, taxpayers can navigate the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 seamlessly, contributing to the overarching goal of fostering a more transparent, efficient, and digitally integrated fiscal environment in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Simplified Tax and Tax Invoice Elements
The authority has provided comprehensive guidance on the key components that constitute these invoices, facilitating clarity and uniformity in financial transactions.
Tax invoice items
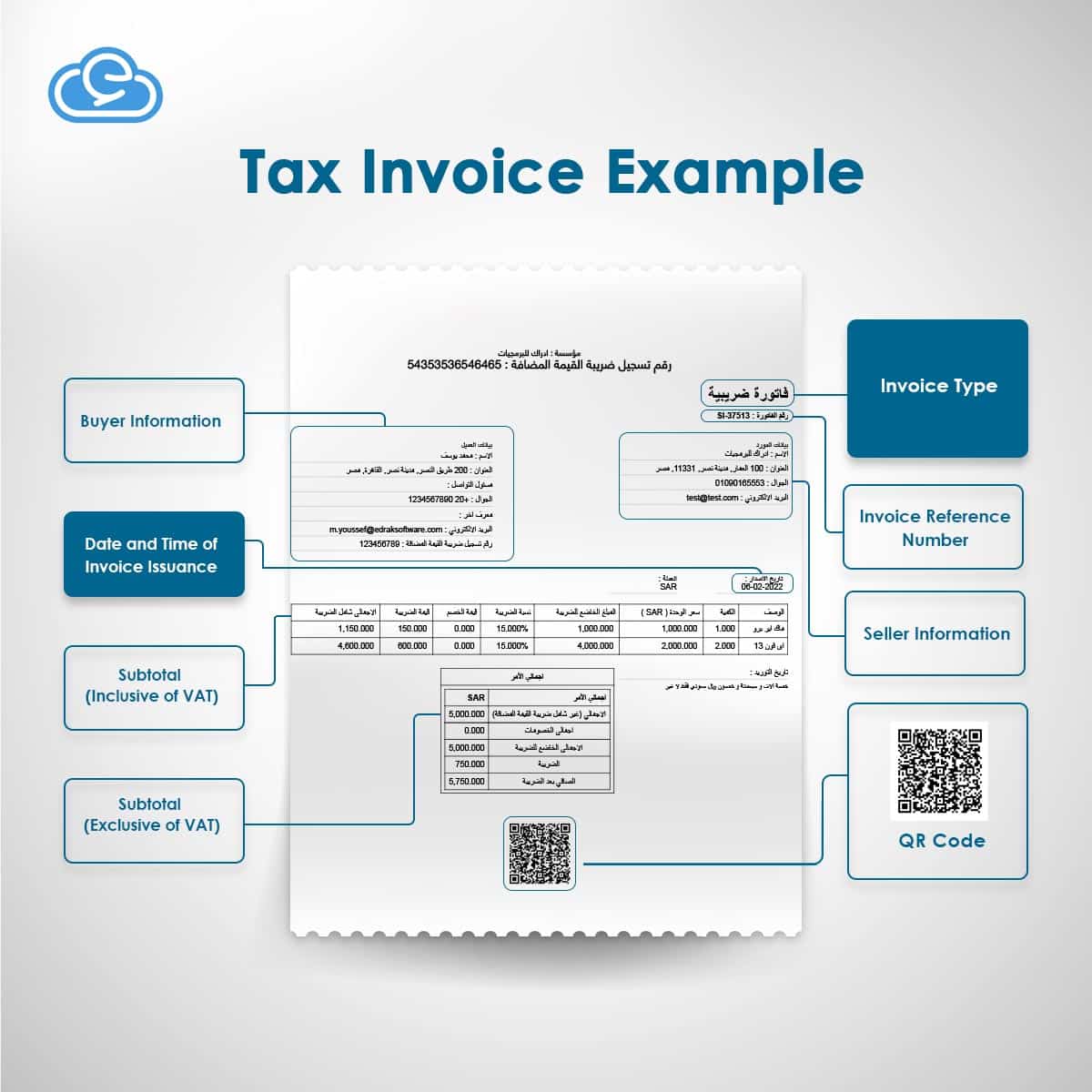
Tax invoices, as elucidated by the Authority, pertain to invoices exchanged between distinct establishments and are composed of the following crucial elements:
- Invoice Address (Tax Invoice)
- Invoice Serial Number:
- Date and Time of Invoice Issuance
- QR Code
- Seller Information
- Buyer Information
- Product Details
- Net Amount (excluding tax) for Each Item
- Tax Rate and Value
- Total Amount (including tax) for Each Item
- Total Net Amount (excluding Value Added Tax)
- Value Added Tax
- Total Amount with Tax
Simplified Tax Invoice Elements

Simplified tax invoices are invoices issued between an establishment and a consumer (B2C), and they consist of:
- Invoice title (simplified tax invoice)
- invoice number
- Store name
- Store address
- Invoice issuance date
- VAT registration number
- Invoice items (mentioning quantity, unit price, and value-added tax for each item)
- Total VAT field
- Total amount, including VAT field
- QR Code
Mechanism of E-invoicing for ZATCA Phase 2
The mechanism of electronic invoicing varies depending on the type of invoice issued and is as follows:
How Electronic Invoicing Works for Tax Invoices
- The seller issues an electronic invoice containing all elements of the tax invoice.
- Share the invoice with the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority.
- Share the invoice with the buyer in a readable format.
- Save the invoice electronically.
How Electronic Invoicing Works for Simplified Tax Invoices
- The seller issues an electronic invoice containing all elements of the tax invoice.
- Submit the invoice to the buyer.
- Save the invoice electronically.
- Share the invoice with the authority within a maximum of 24 hours.
Penalty for Non-Compliance with e-invoicing for ZATCA Phase 2
As of now, the Zakat, Income, and Customs Authority has not officially outlined penalties specifically for individuals failing to adhere to the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2.
However, it is anticipated that such penalties will be announced, following the precedent set in the first phase. In the initial phase, penalties included:
- Fines range from 5,000 to 50,000 riyals for not adhering to the specified electronic invoice format or failing to save invoices digitally.
- A 50,000-riyal fine is imposed for the absence of an encrypted QR code in the simplified tax invoice.
- Establishments may receive a warning or a 50,000-riyal fine for not reporting malfunctions affecting electronic invoice issuance.
- Penalties for unauthorized modification or deletion of electronic invoices vary from 10,000 to 50,000 riyals.
It is advisable for stakeholders to stay informed and vigilant, as official announcements regarding penalties for non-compliance with the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 are expected to be communicated by the Zakat, Income, and Customs Authority in due course.
How Does “Edara” Help You Join the Saudi Electronic Invoicing System?
“Edara” serves as a comprehensive Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) program designed to streamline the management of diverse business departments, encompassing warehouses, sales, purchases, accounts, and fixed assets.
Operating through a centralized interface, this integrated ERP program enables seamless coordination of various functions.
With “Edara,” tracking workflows becomes effortless, accessible from any device and at any time, thanks to its cloud-based features.
The program’s cohesive set of integrated features enhances operational efficiency, and a range of reports provides valuable insights for informed decision-making based on real-time data.
Facilitating integration with popular tools and platforms such as Salla, Shopify, and WooCommerce, “Edara” is not only versatile but also holds accreditation and recognition from the Saudi Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority.
It satisfies all conditions related to the electronic invoicing system, making it an ideal ERP solution for your organization. “Edara” not only simplifies invoicing processes but also ensures full compliance with all regulatory requirements.”
Frequently Asked Questions About the Second Phase of Electronic Invoicing
Similar to any novel system, the KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 gives rise to various inquiries. Some of the most notable ones include:
Can the accounting system employed in the initial phase be utilized once again?
Certainly, the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority has specified that the identical electronic invoice solution from the initial phase can be employed, as long as it is upgraded to meet the requisites of the second phase.
What is the procedure by which the ZATCA informs individuals liable for taxation in the second stage?
The Authority is required to inform those liable for taxation in KSA E-invoicing Phase 2 at least 6 months prior to the implementation date, utilizing either email or SMS notifications.
Are the obligations for taxpayers in the second stage identical to those in the first stage?
Indeed, taxpayers in e-invoicing phase 2 of KSA are expected to adhere to the same requirements as the first stage until the designated implementation date, with the option to voluntarily adopt the requirements of the second stage of electronic invoicing before that specified date.
What happens if I haven’t received notification about Phase 2 requirements?
The Authority does not mandate that the taxpayer adhere to the requirements of the second stage unless they have been officially notified of the assessment date applicable to them.
Conclusion
Saudi Arabia’s second phase of electronic invoicing marks a significant step towards a more effective and inclusive system. Taxpayers must now align with integration requirements on the “Fatoora” platform, impacting various groups with specific invoicing obligations.
Recognizing the pivotal role of approved accounting programs in this transition, selecting an accredited solution is crucial. “Edara” emerges as the ideal choice, streamlining electronic invoicing and ensuring compliance.
For businesses seeking efficiency and compliance, “Edara” offers a seamless solution. Request a demo today to explore its benefits and confidently navigate the evolving fiscal landscape.
References
Related articles
Top 4 Prominent ZATCA-Approved Accounting Software Solutions
Accounting software is a crucial asset for streamlining financial processes and ensuring compliance with tax laws. In the realm of tax compliance in Saudi Arabia, the significance of ZATCA-approved accounting…
